What do the buoys in the water mean?

Buoys are floating markers that act like road signs on the water. They help boaters navigate safely by showing where to travel, where hazards are, where channels begin, and what areas have special rules. Even though buoys float, each one is carefully placed and usually anchored to the bottom. Understanding them is one of the most important skills for safe boating.
1. Lateral Buoys (Channel Markers)
Lateral buoys show the left and right sides of a navigation channel—the safe path a boat should travel.
Red Buoys (“Red Right Returning”)
-
Always kept on your right (starboard) side when returning from open water toward shore.
-
Often shaped like nuns (cone-shaped).
-
Even numbers (2, 4, 6…) that increase as you travel inland.


Green Buoys
-
Kept on your left (port) side when returning from open water.
-
Often shaped like cans (cylindrical).
-
Odd numbers (1, 3, 5…) that increase as you head inland.
A helpful memory tip:
👉 “Red Right Returning”—you pass red on your right when heading upstream or coming back from open waters.
2. Cardinal Buoys (Show Where the Safe Water Is)
Cardinal buoys tell you which direction to go to avoid danger. They use black and yellow colors and special top shapes pointing north, south, east, or west.
-
North Cardinal: Safe water is to the north of the buoy.
-
South Cardinal: Safe water is to the south.
-
East Cardinal: Safe water is to the east.
-
West Cardinal: Safe water is to the west.
These are especially useful near rocks, reefs, or shallow spots where a single buoy must clearly indicate the safe direction.

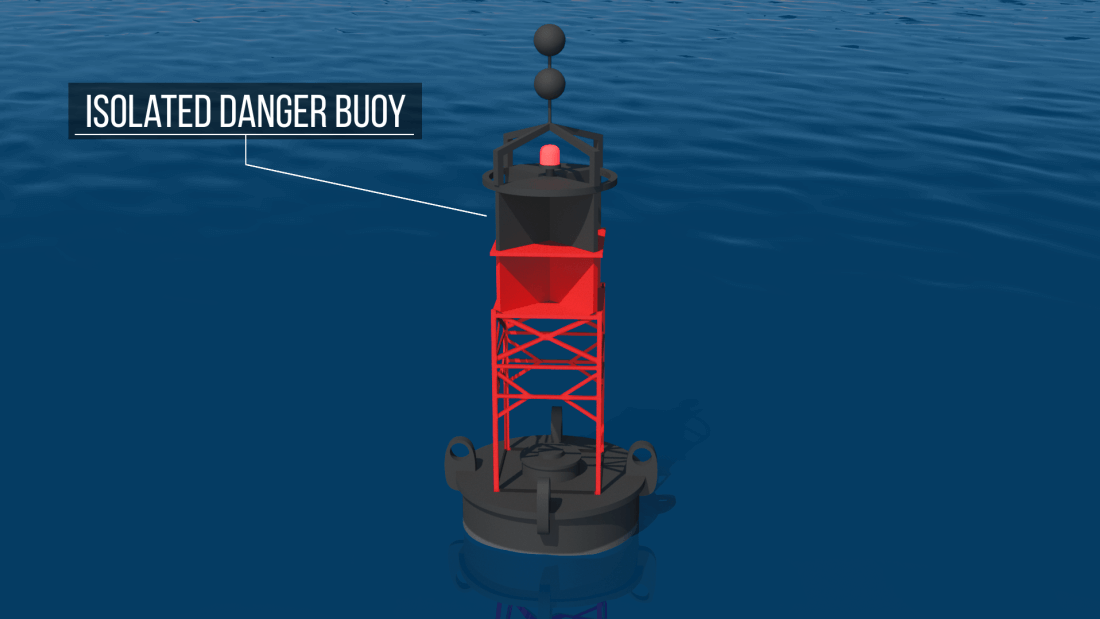
3. Isolated Danger Buoy
This buoy marks a specific danger such as a rock, shipwreck, or sudden shallow area.
-
Colors: Black and red bands
-
Topmark: Two black balls
-
Meaning: “There is danger right here, but safe water all around.”
Boaters simply avoid passing too close to it.
4. Safe Water Buoy
This buoy shows safe, navigable water all around it, often marking the center of a channel, landfall, or mid-channel.
-
Colors: Red and white vertical stripes
-
Often spherical or pillar-shaped
It does not indicate danger—rather, it marks a reference point in safe water.

5. Special Purpose Buoys
These buoys don’t mark navigation hazards. Instead, they mark zones or rules.
They are usually yellow and may indicate:
-
Swimming areas
-
No-wake zones
-
Controlled or restricted zones
-
Military practice zones
-
Research areas
-
Anchoring prohibited
-
Cable or pipeline zones
A yellow buoy always means: Pay attention—special rules here.